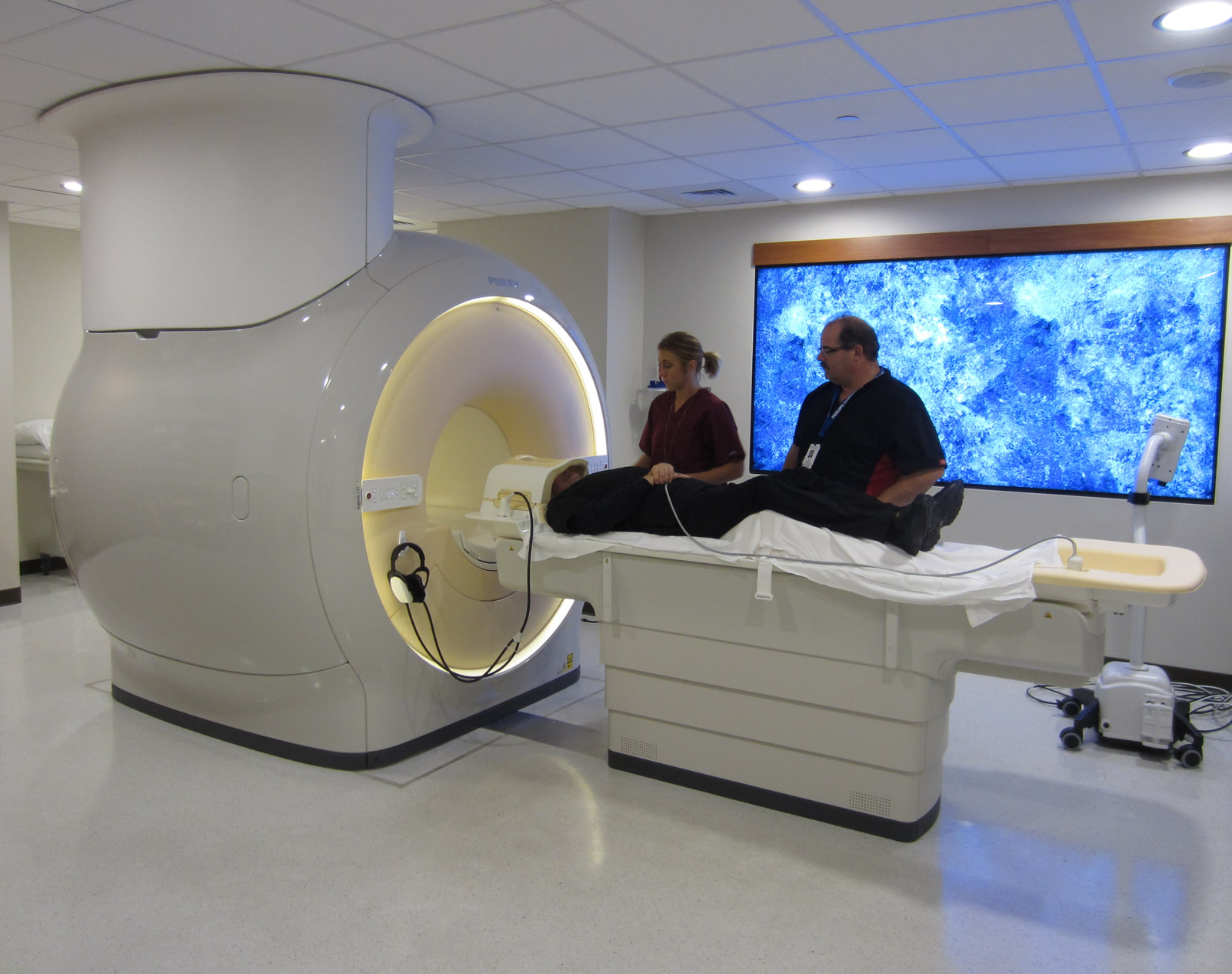
Whittier Imaging
Whittier Imaging offers the latest technology geared toward preventive medicine. Our state-of-the-art Philips MRI scanners offer the most advanced imaging equipment and techniques to screen individuals for underlying disease and also assist your physician in the diagnosis and treatment of known or suspected illness.
Location
Whittier Clinic & Pharmacy
2810 Nicollet Avenue
Minneapolis MN 55408
Frequently Asked Questions about MRIs
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Unlike other radiology procedures that use x-ray radiation, MRI uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to help produce the images of the body. The MRI scanner is able to produce images in any direction with such detail that it has revolutionized medical imaging.
The patient lies on a long table and the large magnetic field surrounds the table. The magnetic field causes the hydrogen protons in the body to align themselves with this magnetic field. A radio frequency is then transmitted through the body causing the hydrogen protons to move. When the radio frequency is turned off, the protons stop moving. As this happens the protons give off a slight signal, which in turn is measured by the computer and transformed into images. Thousands of these signals are measured and processed during a single scan series.
MRI scans can be used as an extremely accurate method of diagnosing diseases in many areas of the body. The exquisite detail produced by these images has made MRI the gold standard for imaging the extremities, especially the joints. In the head, MRI is used to look for tumors, strokes, aneurysms, and nervous system diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis. MRI is considered to be the best exam to look at the entire spine and neck.
Although CT still dominates imaging of the chest and abdomen, MRI is continually coming up with new applications for these body areas and now can be used to evaluate the structures of the heart and aorta as well as the arteries of the abdomen and legs. MRI's ability to look at soft tissue structures has made it one of the newest tools to look at the breast for implant rupture or newly diagnosed breast cancer.
Most MRI exams do not require any fasting before the procedure. Abdomen exams require the patient to not eat or drink for four hours before the test. When you are scheduled for an MRI, it is important to know whether you have any metal objects that have been implanted in the body. The MRI staff will ask you or the scheduler about such things as aneurysm clips and pacemakers.
- Abdomen - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- MRCP - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- Pelvis - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- Abdomen MRA - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- Pelvis MRA - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- Lower Extremity Run-off MRA - Nothing to eat or drink for 4 hours before test.
- All other procedures do not require preparation.
MRI is a painless radiology procedure that has the advantage of not using any x-ray radiation. There are no known side effects of the scan.
However, since the MRI scanner is a large magnet, it is very important to notify the technologist of metal implants and it is necessary to remove all metal objects such as keys and watches before entering the scan room. A screening form must be completed before starting a scan. In some cases, the exam cannot be performed due to certain implants. The most common contraindications for scanning are:
- Cardiac pacemaker
- Implanted defibrillator
- Brain aneurysm clips
- Metal in the eyes
- Implanted devices, such as insulin pumps
- Certain types of ear implants
The technologist will give you a more complete list and can answer any questions you may have before the scan.
The MRI exam may require an injection of a contrast material. The most common contrast is called gadolinium. This basically does the same thing for MRI as iodine does for CT scans. The complication rate for this contrast is very low.
You will be asked to lie on a table and this table will slowly move to the center of the magnetic field. The scanner is a long tube open at both ends. The part of the body being scanned must be in the middle of this tube. Some patients find that they can be somewhat claustrophobic during this scan. However, the Philips scanner has a very short bore and claustrophobia is not usually an issue.
The scanner generates loud knocking noises during the scan so the staff will provide earphones during the procedure. You can listen to your favorite radio station or CD. The scan times are very short and every consideration will be taken to make you comfortable during the procedure.
The procedure usually lasts 15 - 30 minutes and you must lie very still. Some patients like to take a light sedative or pain medication before they arrive for the test.
The exam will be reviewed by your radiologist shortly after the completion of your exam. Some procedures require post processing and can take some time to complete so a report is not always readily available. The Radiologist will dictate a report that will be sent to your referring or primary physician within 24 hours of the procedure.
A complimentary CD-ROM or x-ray film copies of the exam are available to you or your doctor.

